
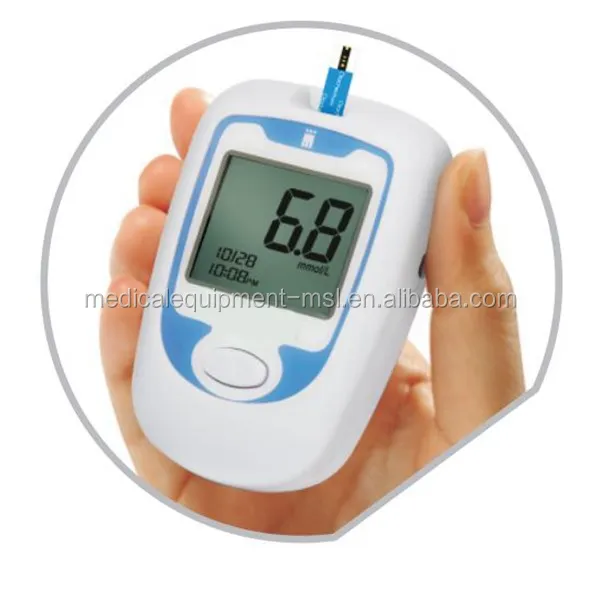
You will also need a finger pricking device with lancets (needles) and blood glucose monitoring strips. Blood glucose metersĪ blood glucose meter uses a small drop of blood to provide you with an immediate BGL. Glucose levels can be monitored using a blood glucose meter, Flash Glucose Monitor (Flash GM) or Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM). If you would like to try structured self-monitoring we have prepared this helpful guide. two weeks) and then working with your diabetes healthcare team to figure out how food, physical activity and medications are impacting your blood glucose levels. Structured self-monitoring involves checking your blood glucose levels at certain times of the day (for instance after meals) for a given period (i.e.

It tells you how you are going with your diabetes self-management which can help increase your confidence.To understand the relationship between your BGLs and medications, food, physical activity and other lifestyle factors such as travel, stress and illness.To know whether your diabetes management plan is right for you.Recording your BGLs to share with your health care team provides important information about your diabetes self-management.This can guide you to know when to seek medical assistance and/or advice from your health care team. Performing finger prick checks gives you an immediate BGL.Why is it important to monitor your BGLs? Monitoring, recording and understanding your blood glucose levels (BGLs), often referred to as blood sugar levels, is important for both you and your health care team. To live well with diabetes, it’s important that you keep your blood glucose levels as close to target range as possible. Blood glucose monitoring can help you to keep your blood glucose level in your recommended target range.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
